What Is 5 Axis CNC Machining? Everything You Need to Know
5-axis machining is one of the most advanced subtractive manufacturing processes available today. By simultaneously controlling 5 axes of motion, it achieves unparalleled efficiency in cutting complex geometries. Unlike conventional 3-axis machines, 5-axis CNC enable multi-angle rotation of the tool or workpiece, drastically reducing setup changes and delivering high-precision, single-setup machining.
What Is 5 Axis Machining?
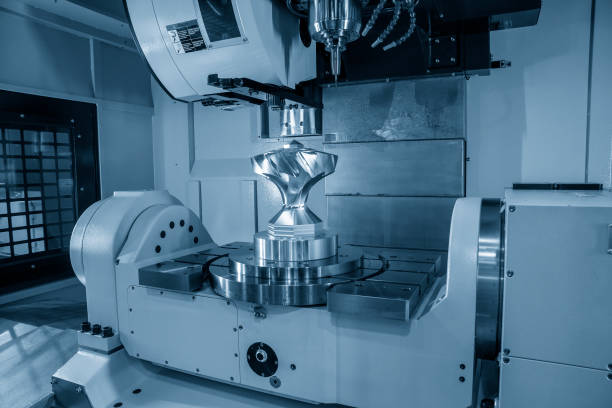

Five-axis machining combines three linear axes (X, Y, and Z) with two rotational axes, allowing cutting tools to move simultaneously along five different axes, enabling the production of highly complex parts with minimal setups.
The key advantage lies in dynamic flexibility. The synchronized movement of 5 axes, including X, Y, and Z linear axes with A/B and C rotary axes, allows the cutting tool to approach the workpiece at optimal angles, enhancing surface finish while extending tool life. For parts requiring undercuts, contoured surfaces, or complex geometries, 5-axis CNC not only shortens production cycles but also eliminates cumulative errors from repositioning, making “complete machining in one setup” a reality.
To better understand the axes of a 5-axis milling machine, let’s first define the machining axis count. The axis count in CNC machining refers to the number of directions in which the cutting tool or workpiece can move to shape the final product. Conventional CNC machines typically have three axes (X, Y, and Z), allowing movement in three directions: back and forth on the Z-axis, vertically on the Y-axis, and sideways on the X-axis.
Five-axis machining enhances this functionality by incorporating two additional rotational axes. These rotational axes can be configured in different ways, resulting in two common setups: AC 5-axis and BC 5-axis.
- AC 5-Axis Configuration: In this setup, the A-axis tilts the worktable, while the C-axis rotates it around the Z-axis. This setup is commonly found in trunnion-style 5-axis machines, where the tilting table provides greater flexibility in machining complex geometries.
- BC 5-Axis Configuration: In this configuration, the B-axis tilts the tool spindle instead of the worktable, while the C-axis provides rotation around the Z-axis. This setup is typically seen in head-head 5-axis machines, offering better accessibility for machining large or heavy parts since the workpiece remains mostly stationary.
With these additional rotational axes, 5-axis machines allow for more precise and efficient machining compared to traditional 3-axis CNC or even 4-axis CNC setups. These machines are ideal for creating complex geometries and features with minimal repositioning, making them highly valuable in aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing industries.
What Does the “5” in the 5 Axis Stand For?
The 5 in 5-axis refers to the fact that machines used for 5-axis machining add two additional axes to the standard three axes—X, Y, and Z—for a total of five axes. A rotates around the X axis, the B axis rotates around the Y axis, and C axis rotates around the Z axis.
Below is a table explaining each axis:
| Axis | Movement |
| X | Left and right (horizontal movement) |
| Y | Front and back (depth movement) |
| Z | Up and down (vertical movement) |
| A | Rotation around the X-axis |
| B | Rotation around the Y-axis |
| C | Rotation around the Z-axis |
Either AC 5 axis CNC or BC 5 axis CNC is available.
5-Axis – Possible Configurations
One of the three rotational axes of the 5-axis CNC Milling Machine will be utilized depending on the selected configuration. A trunnion-style machine and a swivel-rotate-style machine are the two primary configurations.
The A and C axes of a trunnion-style 5 axis CNC mill machine rotate around the X and Z axes, respectively, whereas a swivel-rotate-style 5 axis CNC milling machine rotates the B and C axes about the Y and Z axes, respectively.
The primary distinction between the two is how the rotary axes are expressed: the 5-axis CNC Milling Machine’s swivel-rotate style expresses the rotary axes through spindle swiveling, while the trunnion-type moves the table. Since each has benefits, choosing which to utilize primarily relies on the task at hand. Below is a table showing the possible 5-axis configurations:
| Configuration | Rotary Axes | Description | Pros | Cons |
| Trunnion-Style | A-axis rotates around X-axis, C-axis rotates around Z-axis. | The table moves to achieve 5-axis motion while the spindle remains fixed. | More rigid setup, better for heavy cutting, and supports larger parts. | Table movement limits weight capacity and may require more space. |
| Swivel-Rotate-Style | B-axis rotates around Y-axis, C-axis rotates around Z-axis. | The spindle swivels to achieve 5-axis movement while the table stays mostly fixed. | Handles heavier parts since the table remains stationary, allowing for more compact designs. | Less rigid than trunnion-style machines, leading to potential vibration issues in heavy cutting. |
How Does a 5-Axis CNC Machine Work?
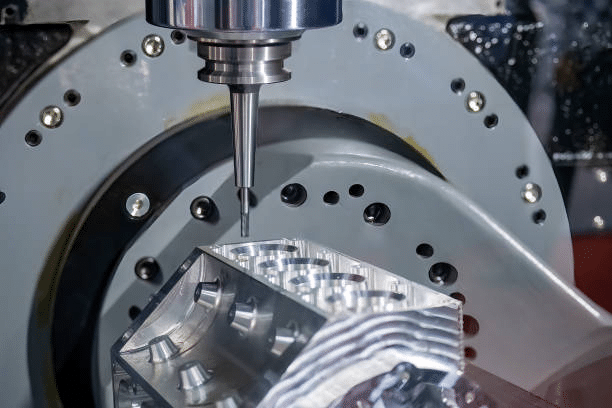
A 5-axis CNC machine operates with high efficiency and precision, requiring minimal human involvement after the setup. The machine uses rotary cutting tools to shape the material placed on its platen. Here’s an expanded breakdown of how it works:
Creating a CAD Design of the Part
The first step in 5-axis CNC machining is designing a part in a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) program. This allows engineers and designers to visualize the shape, size, and structure of parts in 3D and make necessary adjustments before the actual machining. The CAD model serves as a digital blueprint for the part that will be manufactured.
Converting the CAD Design into CAM Software
The CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software takes the digital CAD design and generates the toolpath necessary for the machine to follow. The software optimizes the movements, ensuring that the machine performs the cuts efficiently while minimizing material waste and machining time.
Generating the G-Code
The CAM software converts the toolpath data into G-code, a set of alphanumeric instructions that guide the CNC machine on how to move. The G-code dictates everything from the tool’s speed, path, and feed rate to the specific cutting tool to use for each phase of machining. This code is crucial because it enables the 5-axis CNC machine to perform precise cuts on complex geometries.
Uploading the G-Code to the 5-Axis CNC Machine
Once the G-code is ready, it is uploaded to the 5-axis CNC machine. The G-code acts as a guide for the machine, instructing it on how to execute the precise movements necessary to shape the part. G-code manages the simultaneous rotation of multiple axes, allowing the tool to approach the workpiece from various angles.
Positioning the Material on the Platen
The final step in preparing the 5-axis CNC machine is properly positioning the material on the machine platen. Securely fixed in place to prevent any movement and inaccuracies or part defects during the machining process. This step may involve using jigs or fixtures to hold the material firmly.
Once everything is set up, the 5-axis CNC machine starts machining according to the G-code instructions. With each cut, the machine adjusts the position and orientation of the tool and the workpiece, creating highly detailed and complex parts with a high degree of accuracy.
Benefits of 5-axis Machining
There are various advantages of 5-axis machining and some of them include:
Effective Setup Operations
A 5-axis CNC machine is less complicated than a 3-axis CNC machine in the aspect of the setup. For 5-axis CNC machines can work on five surfaces simultaneously. Furthermore, 5-axis machines can produce parts with complex, curved shapes in a single setup. In contrast, standard 3-axis machines require multiple setups to machine parts with curves or multiple faces.
For a 3-axis machine, you need different cutting tools for each face, like end mills or ball nose cutters, and reposition the part each time to machine different angles. This requires workholding devices to secure the part in each new orientation, which increases setup time and the risk of misalignment. In contrast, a 5-axis machine can perform all cuts without repositioning the part, improving accuracy and efficiency.
Machine Complex Shapes
5-axis machining has several advantages over 3-axis and 4-axis machining, including the capacity to produce complicated pieces. That’s why 5-axis machining is becoming more prevalent in modern manufacturing.
Enhanced range of motion and cutting tool location of 5-axis machines means additional flexibility, higher precision, and accuracy in CNC machining capability for complex designs, which would be difficult or impossible under standard production methods.
High Precision and Repeatability
Manual machining often requires additional settings to ensure optimal machining. These settings may include recalibrating the machine, manually repositioning the workpiece between cuts, or adjusting the tool for each new operation. These steps, while necessary for manual machining, may lead to design variability and errors due to human involvement or misalignment during repositioning.
In contrast, 5-axis CNC cutting requires fewer settings because the machine can simultaneously adjust the cutting tool and workpiece orientation. This significantly reduces the risk of errors and maintains accuracy throughout the process. Furthermore, most modern 5-axis CNC machines automatically reposition the workpiece and adjust the tool orientation, without human intervention during milling, ensuring tighter machining tolerances and more consistent results.
5-axis CNC machines can typically achieve tolerances of ±0.001 mm or even tighter, depending on the machine’s precision and the complexity of the part. In some cases, shorter cutting tools on a 5-axis machine can also improve tool longevity and repeatability, as these tools have less deflection and maintain more stable cutting conditions.
Single Setup
Multiple machine configurations are required to manufacture complex geometry. Compared to 3-axis machines, 5-axis CNC machines have five axes, only once set up for your workpiece is required. The machine will handle every machining operation required to manufacture your desired product.
The once-setup nature of 5-axis CNC machines enables complicated parts rapidly, lower costs, and fewer faults common in traditional CNC machines.
High Production Efficiency
With significantly fewer part machining and auxiliary time, 5-axis machining involves a wide range of spindle speeds and feed rates, allowing the machine a powerful huge cutting capacity. 5-axis CNC is entering a new era of high-speed machining. The quick movement and positioning of 5-axis machining, as well as high-speed cutting processing, shorten the turnaround time for semi-finished goods.
Quality Surface Finish
The additional axes result in a finer surface finish on a 5-axis CNC machine. These extra axes bring the components closer to the cutting tool, thereby making it easier for the desired shapes. It also allows for shorter use of machining tools.
There is little to no vibration with shorter cutting tools, which reduces the risks of marks on the surface of parts. Furthermore, with vertical machining, spindle utilization for miller-inclined surfaces is more efficient.
Drawbacks Of 5-Axis CNC Machining
The 5-axis has several advantages and is very important in the manufacturing of parts. However, not all is rosy with 5-axis machining since certain disadvantages exist. The following are the disadvantages of 5-axis machining:
Increased Cost
A 5-axis CNC machine is significantly more costly than a 3-axis machine. So is the software required to run a machine. Furthermore, It’s more complicated to maintain a 5-axis CNC machine than a CNC machine. As a result, one of the biggest disadvantages of 5-axis CNC machines is the expense.
Programming Complexity
3-axis machines differ from 5-axis machines in programming due to two additional rotational motions, which complicate the synthetic motion’s trajectory.
To minimize collision and interference, It’s necessary to consider each axis’s distinct motion when programming the 5-axis.
High Level of Operator Skill is Required
5-axis CNC machining utilizes cutting-edge technologies. A highly skilled technical operator is necessary to get the most out of the equipment. Hiring a highly skilled operator, on the other hand, enhances labor costs.
Types Of 5-Axis CNC Machines
5-axis machines can improve machining efficiency and scalability. To fulfill the needs of the manufacturing industry, these machining centers might be of numerous types. There are three main types of 5-axis CNC machines:
Head/Head
Rotational axes are situated in the head of head/head machines. Their 5-axis apex is mounted on a platform that moves through a stationary worktable while holding the workpiece in position. As a result, there will be no tool interference on the machine spindle head.
This increases the apex’s ability to move around a workpiece, making it appropriate for creating massive, heavy pieces. The machine table can resist big weights without impairing the rotational aces’ accuracy. However, the architecture of these devices restricts their rotating axis movements.
Head/Table
The head/table machine configuration features one rotational axis in the head and one in the rotary table. Their revolving axis is located in the brain and has a limited range. The rotating shaft, on the other hand, has a larger (infinite) range and is positioned in the table.
This configuration is advantageous since it can spin the workpiece indefinitely. However, there is a limited quantity of parts because the rotary axis supports the workpiece.
Table/Table
The 5-axis machines’ rotating axes are located inside the table in this configuration. As a result, all rotations occur on the table, and the head does not move. These machines’ design makes them ideal for cutting undercuts. Furthermore, because the head does not rotate, machinists can immediately observe the cuts process during the programming step.
However, the machine configuration could be better for CNC milling or CNC turning large or heavy components due to the table’s inability to withstand excessive weight.
| Machine Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
| Head/Head | The rotational axes are in the head, and the spindle moves while the workpiece remains stationary on the table. | No tool interference on the spindle head, suitable for large, heavy parts, and maintains accuracy under heavy loads. | Limited rotational axis movement due to machine design. |
| Head/Table | One rotational axis is in the head, and the other is in the rotary table. The table allows infinite rotation, while the head has a limited range. | Infinite rotation of the workpiece, flexible for various part sizes. | Limited part size capability since the rotary axis must support the workpiece. |
| Table/Table | Both rotational axes are located in the table, while the head remains stationary. | Ideal for cutting undercuts and allows machinists to observe the cuts during programming. | Not suitable for machining large or heavy components, as the table has weight limitations. |
What Type Of Parts Can Be Machined Using A 5-axis Machining Center?
5-axis CNC machining produces a wide range of products. These parts frequently have complex geometries and intricate designs. Here are some examples of 5-axis machining parts:
Special-Shaped Parts
Parts with irregular shapes are referred to as unique-shaped parts. Workpieces have a mix of points, surfaces, and lines, for example. Because of the difficulties in controlling the clamping pressure during the process, It’s difficult or almost impossible to cut such parts by conventional machining. However, 5-axis machining, with a multi-station point, makes the machining easier.
Because of the repeated clamping and alignment required, it’s relatively challenging for standard machining machines to machine box-shaped parts. A 5-axis machine can work on many surfaces at once, making it easier, and more flexible to produce higher-precision box-shaped pieces.
Box Type Parts
Because of the repeated clamping and alignment required, it is difficult to use standard machining equipment on box-shaped items. The ability of a 5-axis machine to work on many surfaces simultaneously makes it easier to produce higher-precision box-shaped pieces.
Disc Parts
5-axis CNC machining is also perfect for machining UAV parts. It is ideal for cutting plate parts and plats, particularly those with end-face distribution holes or radial holes. It is also suitable for producing machine motor covers. It is vital to note that either a horizontal or vertical machining center is used when choosing 5-axis CNC machining. The exact hole direction determines the machining center selected.
Complex Surface Parts
Complex surface parts are common in several industries, such as aviation, aerospace, and electronics. It is tough to achieve this intricate surface with standard CNC machine equipment. Spherical surfaces, turbine engine blades, marine propellers, impellers, and other complicated surfaces produced via 5-axis machining are examples.
Applications Of 5-Axis CNC Machining

Because of its efficiency and capacity to handle complicated shapes, 5-axis CNC machining can be used in a variety of industries. Here are a few examples below:
- Medical-5-axis CNC machining technology is widely used to manufacture orthopedic implants such as artificial joints, bone screws, and spinal screws.
- Energy equipment– It produces rapid prototyping and complex parts such as wind turbine blades and compressor blades. These parts usually have complex geometric shapes and strict dimensional requirements.
- Aerospace– Components such as turbine blades, disks, impellers, casings, as well as wing beams, frames, and ribs of aircraft bodies are extremely complex in shape. Five-axis machines can achieve multi-axis machining, precisely machining these complex surfaces and 3D parts to ensure high precision and quality.
- Automotive- 5-axis CNC machining technology is used to manufacture critical components such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, crankshafts, and connecting rods.
Get Started With 5-Axis Machining At ZCprecision
Before Starting your project, it is crucial to speak with a CNC machining specialist. Globally, zcprecision is a top supplier of CNC machining services. We produce high-precision CNC machined parts with excellent quality, quick lead times, and affordable prices thanks to our CNC machining services.
Our highly qualified professionals also provide technical support to assist you in selecting from our selection of production-grade materials and machining technologies. Get in touch with us right now to discuss your project. Upload your design file to our website to receive a free DFM analysis and a quotation.
Conclusion
Now that you have a thorough understanding of 5-axis CNC machining. Now it is the moment to take control of your manufacturing encounter.
Five-axis CNC machines increase precision and accuracy, expedite and lower manufacturing costs, and streamline fabrication processes. They are not, however, perfect for every design. For example, precise cutouts, holes, and cavities might be better suited and more affordable for 3- or 4-axis CNC machines.
FAQs
Q1: Why Opt for 5-Axis CNC Machining Over 3D Printing?
5-axis CNC machining offers greater precision, material versatility, and efficiency compared to 3D printing.
While 3D printing is excellent for producing complex and special-shaped parts, it lacks the accuracy and surface quality that 5-axis CNC machining can achieve.
CNC machining works well with both plastics and metals, whereas 3D printing is primarily suited for plastics and select metals.
Additionally, 5-axis machining is more suitable for on-demand production since it delivers faster turnaround times and stronger parts.
Unlike 3D-printed components that may suffer from weak layer bonding, CNC-machined parts are cut from a solid block, ensuring superior structural integrity.
Q2: What’s the Main Difference Between 5-Axis CNC Machining and 3+2 Axis CNC Machining?
The key difference lies in the movement of the cutting tool. In 5-axis CNC machining, the tool moves continuously along five axes, allowing for smooth, complex surface machining with minimal repositioning. This method is ideal for high-precision parts with intricate geometries.
In contrast, 3+2 axis CNC machining locks the tool in a fixed, tilted position before cutting begins. While it allows access to multiple faces of a part, it does not offer continuous movement, making it less efficient for complex, freeform surfaces.
Q3: How Many Axes Can a CNC Have?
A three-dimensional object has six faces, and a 5-axis CNC machine can process the most faces in a single setup. Machines with more than five axes exist, such as 6-axis and 7-axis CNC machines, but they require more complex programming and are generally unnecessary for most applications. Adding more axes increases machine control but often leads to diminishing returns in efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For most precision machining tasks, 5-axis technology remains the optimal balance between capability and practicality.






